Infrared spectroscopy (IR) is a powerful analytical technique used to study the vibrational modes of molecules. This technique is widely used in chemistry, biology, and material science to identify and quantify chemical compounds, study chemical reactions, and analyze the molecular structure of materials.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the principles of IR spectroscopy, the instrumentation involved, and its various applications.
Principles of IR Spectroscopy
IR spectroscopy is based on the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter. When a molecule is exposed to IR radiation, it absorbs specific frequencies that correspond to the vibrational modes of the molecule. These vibrations can occur in different ways, including stretching and bending of chemical bonds, and deformation of molecular shapes.
The frequency of the absorbed IR radiation is directly proportional to the strength of the bond and the mass of the atoms involved. Therefore, the IR spectrum of a compound can provide information about the functional groups present and the molecular structure of the compound.
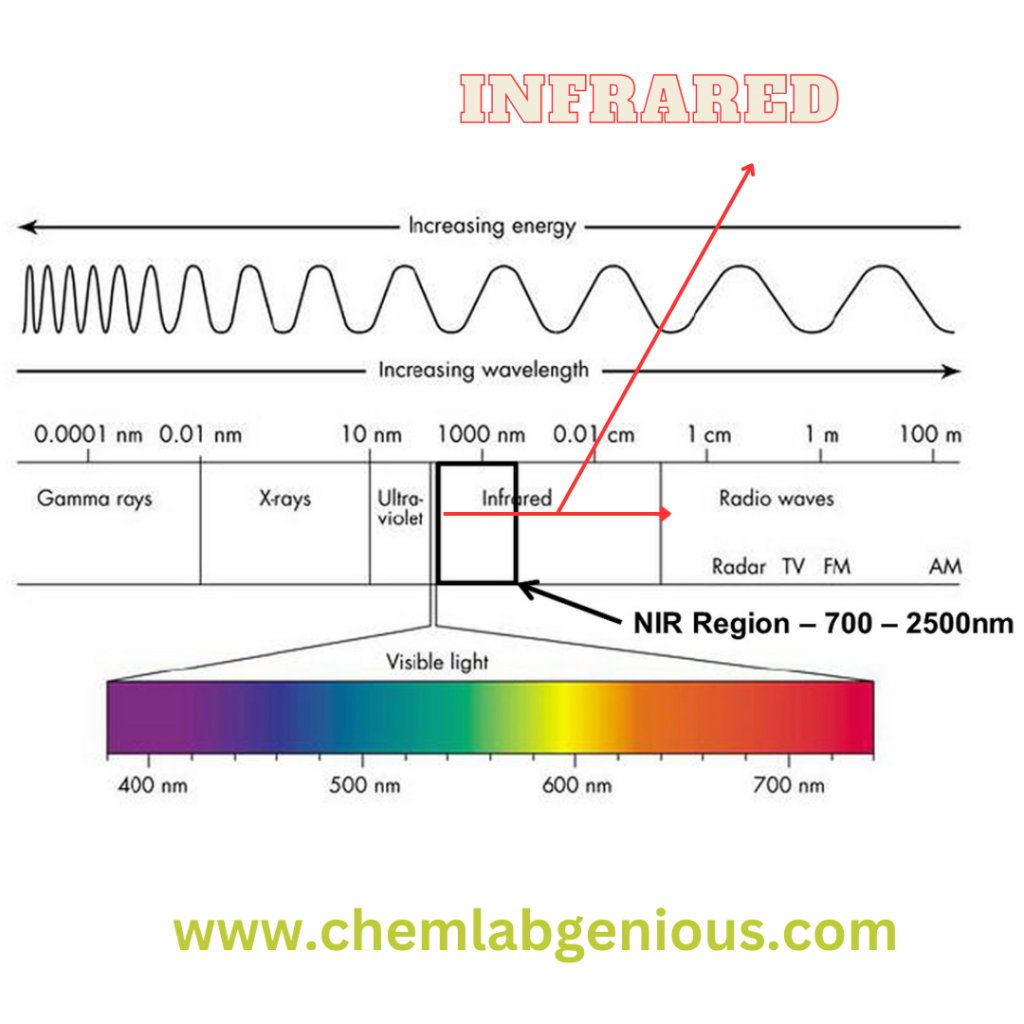
Instrumentation for IR Spectroscopy
The basic components of an IR spectrometer include a source of IR radiation, a sample holder, a detector, and a data analysis system. The IR source emits radiation over a range of frequencies, typically between 4000 and 400 cm-1. The sample holder can be either a liquid or solid, and the detector can be a thermocouple or a photoconductive device.
Modern IR spectrometers also include additional components, such as interferometers and Fourier transform algorithms, which allow for more precise and efficient data collection and analysis.
Applications of IR Spectroscopy
IR spectroscopy is widely used in various fields for a range of applications. In organic chemistry, it is used to identify functional groups and determine the purity of compounds. In biochemistry, it is used to study the structure and function of proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. In materials science, it is used to analyze the molecular structure of polymers, ceramics, and glasses.
IR spectroscopy is also used in forensics and criminal investigations to analyze trace evidence and identify unknown substances. Moreover, it is a valuable tool in environmental monitoring and industrial quality control.
Types of samples in IR Spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR) is a versatile analytical technique that can be used to analyze a wide range of samples. Here are some common types of samples analyzed using IR spectroscopy:
- Solids: Solid samples can be analyzed using IR transmission or reflection techniques. Samples can be in the form of powders, films, or pellets. Common examples include polymers, minerals, and pharmaceuticals.
- Liquids: Liquid samples are typically analyzed in transmission mode. The liquid is placed between two IR-transparent plates, such as KBr or NaCl crystals, to form a thin film. Common examples include solvents, oils, and chemical solutions.
- Gases: Gas samples can be analyzed using IR spectroscopy by passing the gas through a gas cell, which is a long, narrow chamber with windows on either end that allow IR radiation to pass through. The gas cell is filled with a suitable IR-transparent gas, such as carbon dioxide or nitrogen, to create a uniform background.
- Films: Thin films, such as those used in coatings or adhesives, can be analyzed using IR transmission or reflection techniques. The film is placed between two IR-transparent plates, such as KBr or NaCl crystals, to form a thin film.
- Biological samples: Biological samples, such as tissues, cells, and proteins, can be analyzed using IR spectroscopy. These samples are typically analyzed in transmission mode, and the sample preparation can vary depending on the specific biological sample.
Conclusion
Infrared spectroscopy is a versatile and powerful technique that provides valuable information about the molecular structure of compounds. Its broad range of applications in various fields makes it an essential tool for scientific research and analysis.
Whether you are a student, a researcher, or a professional in the field, understanding the principles and applications of IR spectroscopy can greatly enhance your understanding of chemistry and related fields.
FAQ’s of IR Spectroscopy
Q: What is IR spectroscopy?
A: IR spectroscopy is an analytical technique used to identify and analyze the molecular structure of a substance based on its interaction with infrared radiation.
Q: How does IR spectroscopy work?
A: IR spectroscopy works by passing infrared radiation through a sample and measuring the absorption or transmission of the radiation by the sample. The absorption or transmission spectrum is then used to identify the chemical functional groups present in the sample.
Q: What are some common applications of IR spectroscopy?
A: IR spectroscopy is widely used in chemistry, biochemistry, materials science, and pharmaceuticals for identifying and analyzing the molecular structure of compounds. It is commonly used in the analysis of polymers, oils, pharmaceuticals, and organic compounds.
Q: What is the difference between FTIR and dispersive IR spectroscopy?
A: FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared) and dispersive IR spectroscopy are two different types of IR spectroscopy. The main difference between the two is the way the infrared radiation is measured. In FTIR, the radiation is measured using an interferometer, while in dispersive IR, the radiation is measured using a prism or grating.
Q: What is the advantage of FTIR over dispersive IR spectroscopy?
A: FTIR has several advantages over dispersive IR spectroscopy, including higher sensitivity, faster data acquisition, and improved accuracy. FTIR is also less affected by external factors, such as temperature and vibration.
Q: How is sample preparation important in IR spectroscopy?
A: Sample preparation is critical in IR spectroscopy as it can affect the accuracy and reliability of the analysis. Samples should be prepared carefully to ensure that they are homogeneous, free from contamination, and in the correct form for the analysis.
Q: What are some common sample forms used in IR spectroscopy?
A: Some common sample forms used in IR spectroscopy include powders, films, pellets, and liquids. The sample form will depend on the type of analysis and the IR technique used.
